Delphinol Blood Sugar Stabilizing Support
DELPHINOL® LOWERS OXIDISED LDL CHOLESTEROL IN CIGARETTE SMOKERS
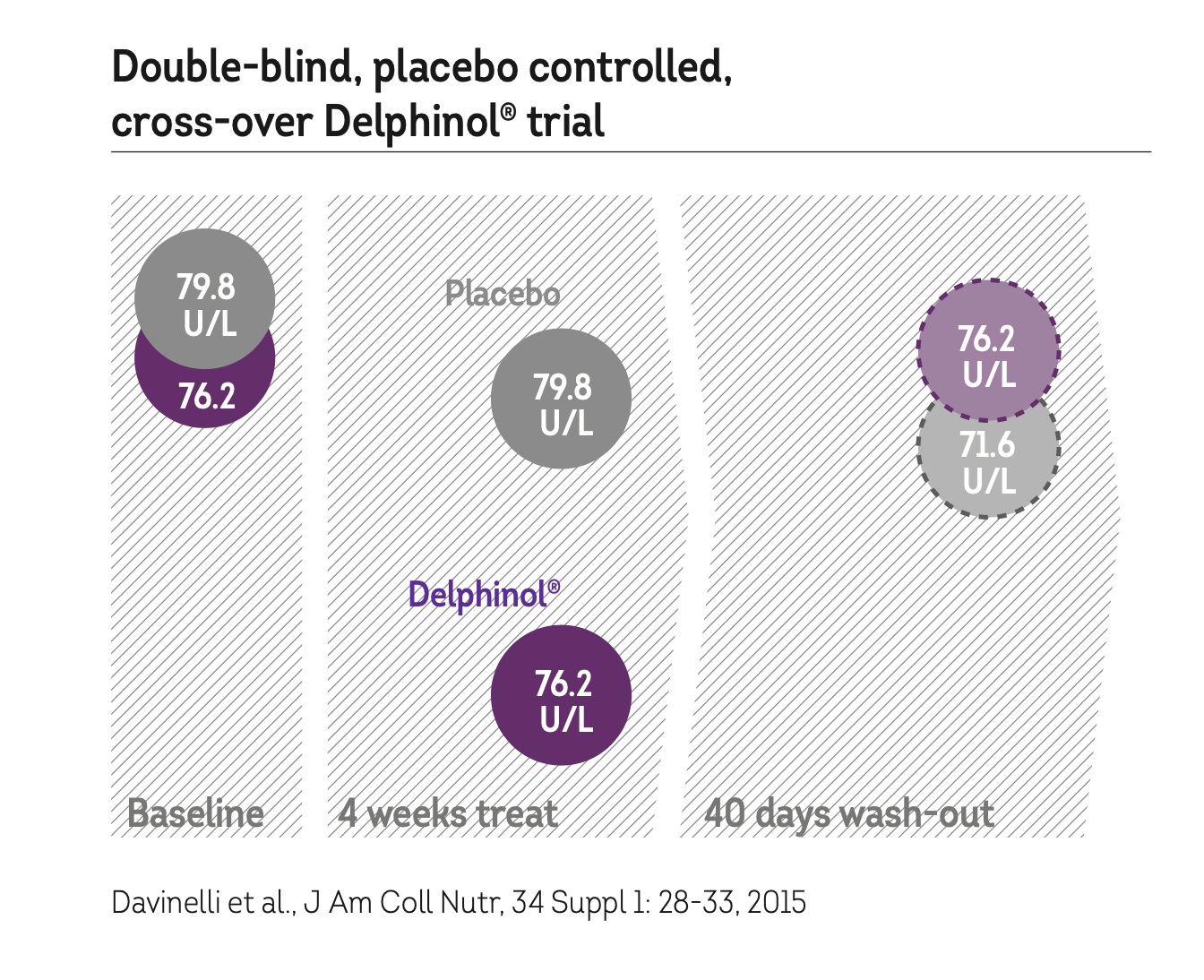
The antioxidant virtues of DELPHINOL® have been demonstrated in a double-blind, placebo-controlled, cross-over study with 50 over-weight cigarette smokers.
Subjects received 150 mg Delphinol capsules, three times a day, or placebo. There was a wash-out period of four weeks during which the subjects crossed- over to opposite regimen.
Blood plasma oxidised LDL in 42 smokers
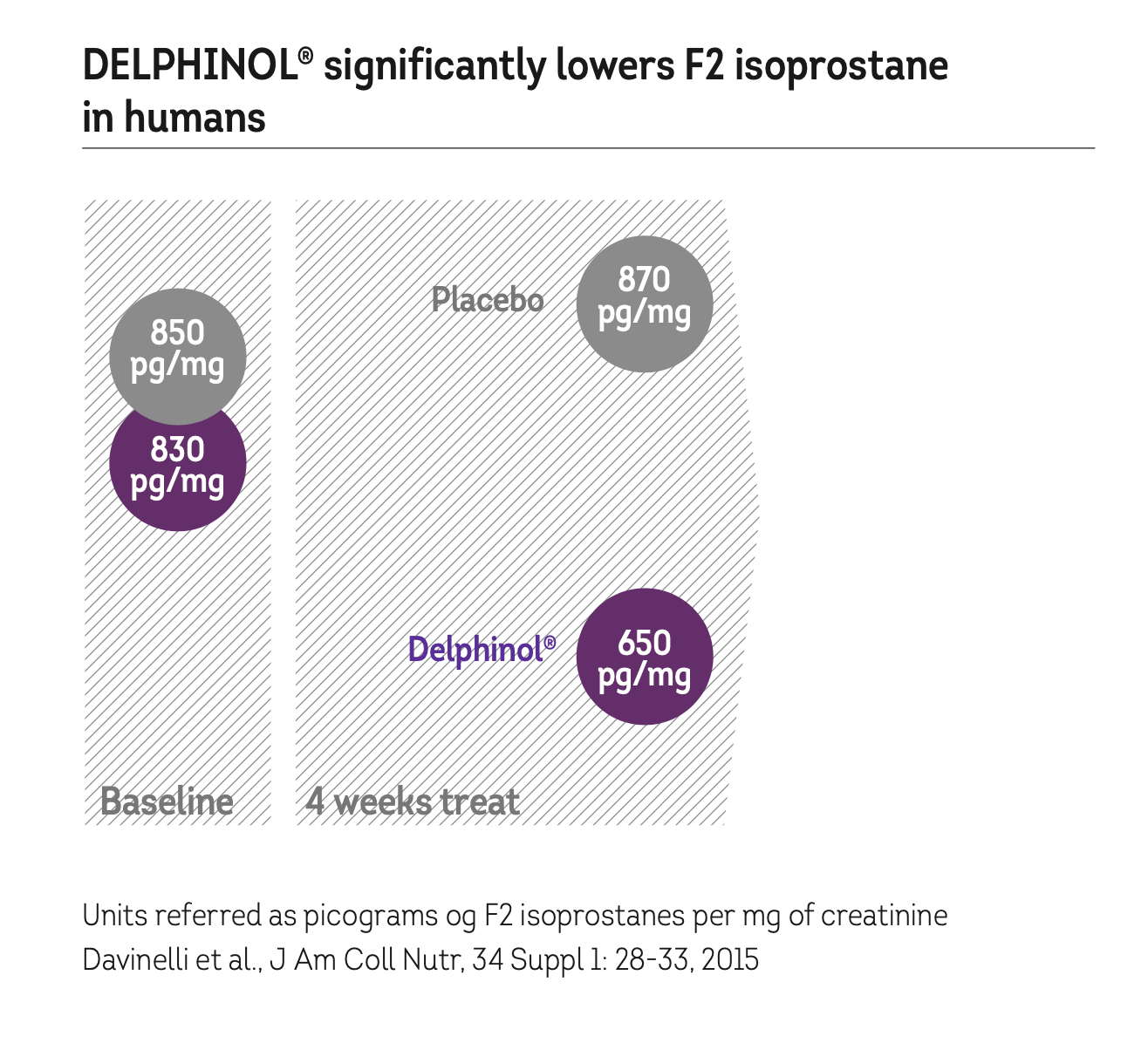
Urinary F2 isoprostanesper ng/mg creatine
F2 isopostane is a validated marker for oxidative stress in humans.
F2 isoprostanes develop when reactive oxygen radicals oxidise poly-unsaturated fatty acides (arachidonic acid).
F2 isoprostanes are removed from the body with urine.
DELPHINOL® METABOLISM
Helps Maintain Glucose Balance
DELPHINOL® extract stabilizes blood glucose levels, helping to control metabolic balance.
The delphinidins of DELPHINOL® have powerful anti- inflammatory effects due to their activation of the PPAR gamma receptor. This activation mechanism is strongly correlated with the control of Type 2 diabetes since it enhances insulin sensitivity.
Also, since hyperglycemic episodes in diabetic patients are closely linked to nitro-oxidative or oxidative stress —the most important factor in the onset and progress of vascular and kidney complications from Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes— the potent effect of DELPHINOL® may help prevent the pro-oxidant effects of hyperglycemia.
In conclusion, studies show that the delphinidins of DELPHINOL® significantly increase the expression of adipocytokine genes, PPAR gamma and specific adipocyte genes in humans and can be an excellent complement to regulate the adipocyte function.
Pre-Clinical Studies and Toxicology
DELPHINOL® has been subject to pre-clinical trials carried out by senior researchers and collaborators at the Institute of Pharmacology and Morphophysiology at Universidad Austral de Chile, in the city of Valdivia. In these trials, the extract was shown to have anti-aging characteristics, including anti-oxidant, immune-boosting, anti-inflammatory and glycaemia control characteristics.
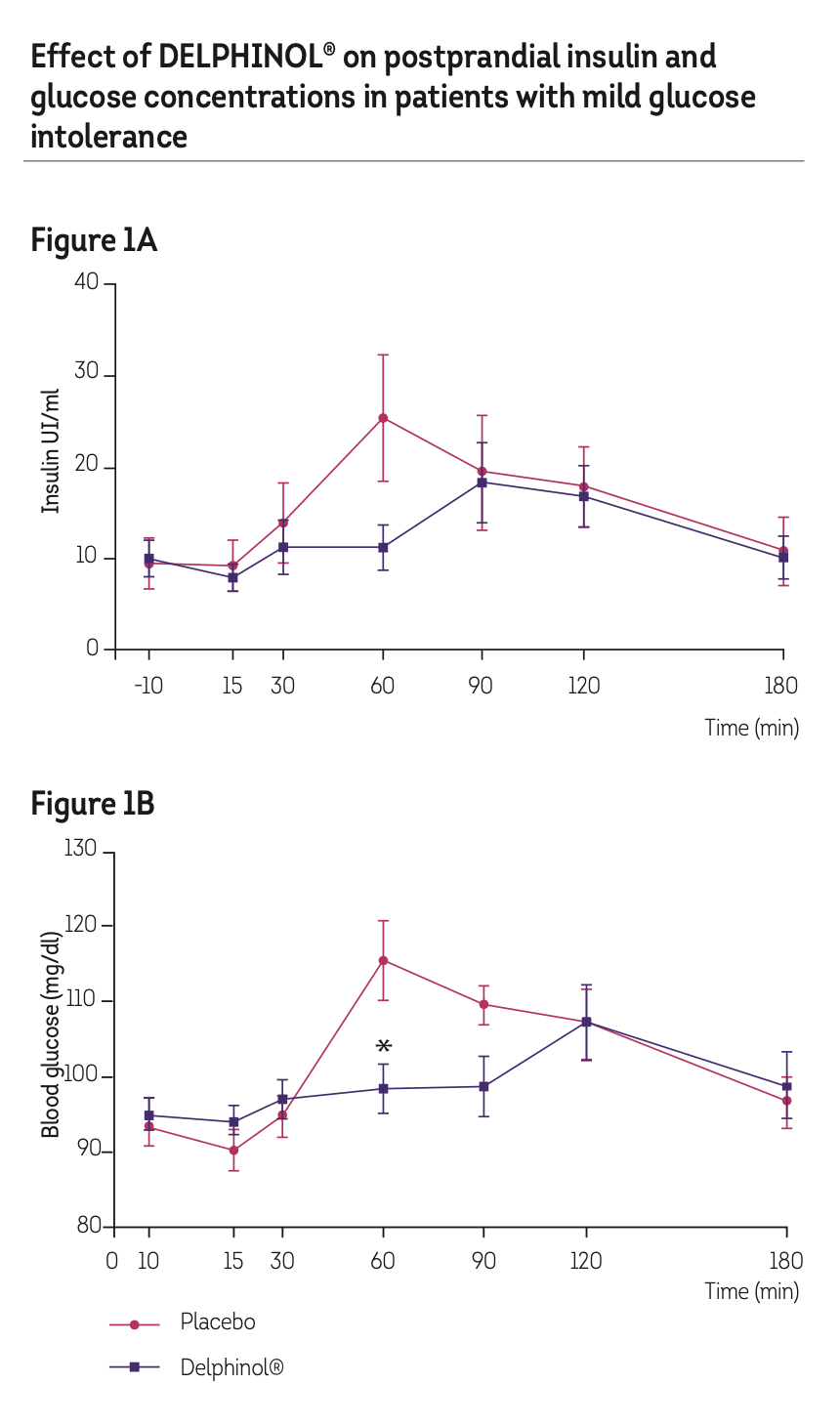
Twelve adult patients of both sexes were enrolled and divided in 2 groups of 6, separated by a 7 day washout, with ages between 18 and 55 years not receiving any acute or chronic pharmacological therapy and a body mass index (BMI) inferior to 30 kg/m2 with a fasting plasmatic glucose (BG) <110 mg/100 mL and an altered glucose tolerance test (110 to 125 mg/100 ml) 120 minutes after the intake of 75 grams of carbohydrates (cooked white rice, grade 1). In each session, all patients received a glass of water containing, either a placebo or 200 mg of DELPHINOL® powder dissolved in water as a single dose after a 12 h fasting period. The patients were crossed in the second week, receiving the other product. Each time, placebo and DELPHINOL®, received 30 minutes before, a meal (defined as a fixed quantity of 75 g cooked white rice grade 1). The dose of the product and placebo was studied in the patients during 4 sessions. The period of wash out/ time interval between the different administrations was 6 days. Session 1 = Placebo. Session 2 =200 mg DELPHINOL®. The first sample was taken as the base line 10 minutes before (time -10) to the treatment with DELPHINOL® or Placebo (time 0); the second sample, 15 minutes after the intake of the product (time +15). The rice was served 30 minutes after the intake of DELPHINOL® or placebo, the third sample obtained at the same moment (time +30). Then, consecutive blood samples were taken at times, +60, +90, and +120 and +180 minutes after the intake of the product or placebo and calculated using the blind individual crossover (“Standard Glucose Tolerance Test”).
The results show that a single administration of DELPHINOL® leads to alterations in the shape of the curves of insulin (see Figure 1A) and glucose (Figure 1B). Patients receiving 200 mg DELPHINOL® had significantly reduced postprandial glucose after 30 minutes following administration of a meal, compared to patients receiving only placebo. Also, kinetic results show a shift in the time when glucose and insulin reached its maximum post prandial peak in patients with the extract (Figure 1A), that correlated with a late decrease in the levels of glucose (Figure 1B).
DOSE-RESPONSE CLINICAL STUDY WITH PRE- DIABETIC PARTICIPANTS
Participants with impaired glucose metabolism (pre-diabetes)
Included 36 pre-diabetic participants:
Women and men ages 18-50, BMI > 23 kgm-2.
Inclusion criteria:
A basal (stable-overnight) blood glucose concentration greater than 100 mg/dL, or basal insulin > 15μU/mL.
Blood glucose values reaching or exceeding 160 mg/dL at any time.
A blood glucose value persisting at ≥ 140 mg/dL over two hours, or insulin values persisting at ≥ 60 μU/mL, for a continuous time period of 120 minutes.
This graph in brief present the dose-effect size of the three dosages on fasting glucose (similar to the previous slide) and also shows the blood sugar values 30 minutes after consumption of 75 grams of glucose.
Again, here is a noticeable difference that the first 60 mg shows the greatest impact, while doubling the dosage does not lower glucose twice as much, and the values for 120 and 180 essentially stay the same.
And the values for 120 and 180 are essentially of the same size.
3 MONTH CLINICAL STUDY WITH PRE-DIABETIC PARTICIPANTS
Participants with impaired glucose metabolism (pre-diabetes)
Included 36 pre-diabetic participants:
Women and men aged 18-50 years, BMI > 23kgm-2
Inclusion criteria:
A basal (stable-overnight) blood glucose concentration greater than 100 mg/dL, or basal insulin > 15 μU/mL.
Blood glucose values reaching or exceeding 160 mg/dL at any time.
A blood glucose value persisting at ≥ 140 mg/dL over two hours, or insulin values persisting at ≥ 60 μU/mL, for a continuous time period of 120 minutes
A DELPHINOL® dose-finding study for effects on glucose-control has been carried out with 36 pre- diabetic individuals.
Prediabetic people were chosen because they respond with higher blood glucose after consumption of a defined amount of glucose.
REGULAR DELPHINOL® INTAKE SHOWS LASTING BLOOD GLUCOSE LOWERING
The antioxidant virtues of Delphinol were tested in the overweight individuals by measuring the quantities of oxidised LDL in their blood. Oxidised LDL is an important health parameter because the oxidised LDL sticks to artery wall, where additional bound LDL may, wuth time, generate an atherosclerotic plaque.
The average value of glycated hemoglobin of the 36 volunteers was 5.65 at the begining of the trial (baseline). Every 30 days of treatment the levels of HbA1c were measured again and a drop of the values was found.
After 60 days of delphinol supplementation the drop on HbA1c reached statistical significance.
During the same study we observed an improvement on lipidinc profile.
Total Cholesterol decreases after 3 months of diet supplementation with Delphinol®.
HDL values, also known as “good cholesterol” experience a statiscally significant increase since the second month of supplementation.
LDL values, also known as “bad cholesterol” experience a statiscally significant decrease since the third month of supplementation.